IDENTIFICATION OF FUNGI
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
IDENTIFICATION OF FUNGI
Specimen collection
Specimens for fungal microscopy and culture may be:
Scrapings of scale, after cleaning with alcohol.
Skin stripped off with adhesive tape, which is then stuck on a glass slide.
Hair which has been pulled out from the roots.
Brushings from an area of scaly scalp.
Specimens for fungal microscopy and culture may be:
Nail clippings.
Skin biopsy.
Moist swab from a mucosal surface (inside the mouth or vagina) in a special transport medium.
A swab should be taken from pustules in case of secondary bacterial infection.
Morphology Direct Microscopy
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) stained with blue or black ink.
Unstained wet-mount.
Stained dried smear.
Histopathology of biopsy with special stains.
Types of fungi
A.Molds (filamentous fungi)
B.Yeasts (bacteria-like fungi)
Types of fungi
Molds (filamentous fungi)
consist of long, branching filaments of cells called hyphae (singular hypha).
a mass of hyphae visible to the unaided eye is a mycelium (plural, mycelia).
In some molds, cross walls may occur along the hypha. Those fungi that have cross walls are called septate fungi, since the cross walls are called septa.
Reproduction in fungi is by spores.
Spores are produced by either sexual or asexual means.
Asexual spores may be free and unprotected at the tips of hyphae, where they are called conidia.
Asexual spores may also be formed within a sac, called sporangiospores.
B.Yeasts
are microscopic.
unicellular fungi with a single nucleus and eukaryotic organelles.
They reproduce asexually by a process of budding
Molds (filamentous fungi)
Molds (filamentous fungi
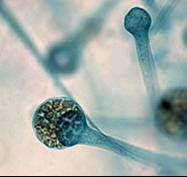
Aspergillus

Aspergillus
Rhizopus
Rhizopus

Penicillium
Penicillium
Penicillium

Candida albicans

Candida albicans

Culture
Sabouraud's Dextrose agar
Used to culture fungi
High %age of glucose
Has a low pH that inhibits the growth of most bacteria;
May also contains the antibiotic gentamicin to specifically inhibit the growth of Gram's-negative bacteria
Potato Dextrose agar
PDA is used to culture of certain types of fungi
Cultivation of fungi is mostly at lower temperature and longer time than that for bacteria
Temperature preferably at room temperature (~24oC).
Time for incubation 3 – 14 day
Other Diagnostic Tools
Polymerase Chain Reaction Definition
Is a technique widely used in molecular biology.
Used for quickly "cloning" a particular piece of DNA in the test tube, and
searching for genes of interest
It can only replicate fairly small pieces of DNA
PCR allows early diagnosis of malignant diseases such as leukemia and lymphomas.
PCR also permits identification of non-cultivatable or slow-growing microorganisms such as mycobacteria, anaerobic bacteria or viruses.
The basis for PCR diagnostic applications in microbiology is the detection of infectious agents and the discrimination of non-pathogenic from pathogenic strains by virtue of specific genes.
PCRs have a variety of uses, including “genetic fingerprinting” at the crime scene.
This is often critical for forensic analysis,, when only a trace amount of DNA is available as evidence.
PCR machine (thermal cycler)





Is a technique widely used in molecular biology.
Used for quickly "cloning" a particular piece of DNA in the test tube, and
searching for genes of interest
It can only replicate fairly small pieces of DNA
PCR allows early diagnosis of malignant diseases such as leukemia and lymphomas.
PCR also permits identification of non-cultivatable or slow-growing microorganisms such as mycobacteria, anaerobic bacteria or viruses.
The basis for PCR diagnostic applications in microbiology is the detection of infectious agents and the discrimination of non-pathogenic from pathogenic strains by virtue of specific genes.
PCRs have a variety of uses, including “genetic fingerprinting” at the crime scene.
This is often critical for forensic analysis,, when only a trace amount of DNA is available as evidence.
PCR machine (thermal cycler)


PCR Accessories


PCR
DNA amplification takes place in small tubes placed into a PCR machine.
It is basically a heating and cooling block.
The mix in the tubes initially contains a small amount of Genomic DNA, Taq polymersae, primers, salts, buffers, and extra G's, A's, T's and C's that are added on while the DNA pieces are built.
Once the cycles finish we visualize the reactions to see if they worked by running a small amount out on an agarose gel.
PIC
DNA amplification takes place in small tubes placed into a PCR machine.
It is basically a heating and cooling block.
The mix in the tubes initially contains a small amount of Genomic DNA, Taq polymersae, primers, salts, buffers, and extra G's, A's, T's and C's that are added on while the DNA pieces are built.
Once the cycles finish we visualize the reactions to see if they worked by running a small amount out on an agarose gel.
The mix in the tubes initially contains a small amount of
Genomic DNA, DNA segment to be copied
Taq polymersae, extracted from a deep-sea, thermal bacterium, Thermus aquaticus.
primers,
salts,
Buffers,
DNA nucleotides to serve as feedstock .
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) (for reading)
The reaction mixture for a PCR test contains the target DNA to be amplified, two primers, and heat-stable Taq polymerase.
Nucleic acid from the m.o. (double-stranded DNA) is denatured by heating to 95°C.
Two short single-stranded primers (DNA fragments that are complementary) bind to the separated DNA strands when the temperature is lowered to 55°C. The primers are extended with Taq polymerase which brings in new nucleotides to build new DNA strands at 72°C.
PCR FOR READING
The first synthesis cycle results in two copies of the target DNA sequence. The cycle is repeated (denaturation, annealing, and extension), and the second synthesis cycle results in four copies of the target DNA sequence. The billions of copies of the new DNA strands that are produced during 40 PCR cycles are detected using gel electrophoresis.
CYCLES
In presence of polymerase enzyme (heat resistant) separation of a double stranded DNA (parentral strands) by heat at 95 degrees.
o Annealing: Synthetic pair of oligonucleotide probes are allowed to attach to their matching base sequences on the separated DNA helicals.
o Since DNA polymerase is not denaturated by heat, its presence will allow the small synthesized oligonucleotide probe to extend along the specific DNA fragment – sort of replication-.
o This 3 step cycle is repeated 25 to 35 times.













thanks
ReplyDeleteI'd like to find out more? I'd love to find out some additional
ReplyDeleteinformation.
My blog post - bmi chart for men