General laboratory findings in clinical toxicology
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
General laboratory findings in clinical toxicology
1- Routine
biochemical analysis: blood glucose, Electrolytes, blood
gases, pH, plasma enzyme and
Cholinesterase activity.
2- Hematological
analysis: hematocrit, blood clotting, leukocyte count.
3- Clinical
toxicology analysis: therapeutic drugs and drugs of abuse
1-Biochemical
tests:
(a)
Blood glucose
● Marked hypoglycaemia often results from
overdosage with antidiabetic drugs.
● Hypoglycaemia may also complicate severe
poisoning with a number of agents
including iron salts and certain fungi.
● Hyperglycaemia is a less common
complication of poisoning than hypoglycaemia, but has been reported after
overdosage with acetylsalicylic acid, salbutamol and theophylline
(b)
Electrolytes, blood gases and pH
● Acid-base and electrolyte disturbances
occur in many types of poisoning for a variety of reasons:
● Coma resulting from overdosage with
hypnotic, sedative, neuroleptic or opioid drugs is often characterized by
hypoxia and respiratory acidosis.
● overdosage with salicylates such as
acetylsalicylic acid initially causes hyperventilation and respiratory
alkalosis, which may progress to the mixed metabolic acidosis and hypokalaemia
characteristic of severe poisoning.
● Hypokalaemia and metabolic acidosis are
also features of theophylline and salbutamol overdosage.
● Hyperkalaemia or hypernatraemia occurs in
deliberate overdosage with potassium or sodium salts.
● Hyponatraemia can result from many causes,
including water intoxication, inappropriate loss of sodium, or impaired
excretion of water by the kidney.
● Hypocalcaemia can occur in ethylene glycol
poisoning owing to sequestration of calcium by oxalic acid
c) Plasma enzymes
● Shock, coma, and convulsions are often
associated with nonspecific increases in the plasma or serum activities of
enzymes (lactate dehydrogenase, GOT, GPT) commonly measured to detect damage to
the major organs.
● The plasma activities of liver enzymes may
increase rapidly after absorption of toxic doses of substances that can cause
liver necrosis, notably paracetamol, carbon tetrachloride, and copper salts.
● Chronic ethanol abuse is usually associated
with increased plasma gamma-glutamyltransferase activity.
(d)
Cholinesterase activity
● Systemic toxicity from carbamate and
organophosphorus pesticides is due largely to the inhibition of
acetylcholinesterase at nerve synapses.
● Cholinesterase, derived initially from the
liver, is also present in plasma, but inhibition of plasma cholinesterase is
not thought to be physiologically important.
● It should be
emphasized that cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase are different enzymes:
plasma cholinesterase can be almost completely inhibited while erythrocyte
acetylcholinesterase still possesses 50% activity
● In
practice, plasma cholinesterase is a useful indicator of exposure to
organophosphorus compounds or carbamates, and a normal plasma cholinesterase
activity effectively excludes acute poisoning by these compounds.
● Erythrocyte (red cell) acetylcholinesterase
activity can be measured, but this enzyme is membrane-bound and the apparent
activity depends on the methods used in solubilization and separation from
residual plasma cholinesterase.
● At present there is no standard procedure.
However, low activities of both plasma cholinesterase and erythrocyte
acetylcholinesterase is strongly suggestive of poisoning with either
organophosphorus or carbamate pesticides.
2-
Haematological tests
(a) Blood clotting
● Prolonged prothrombin time is a valuable
early indicator of liver damage in poisoning with metabolic toxins such as
paracetamol.
● The prothrombin time and other measures of
blood clotting are likely to be abnormal in acute poisoning with rodenticides such
as coumarin anticoagulants, and after overdosage with heparin or other
anticoagulants.
● Coagulopathies may also occur as a
side-effect of antibiotic therapy.
(b)
Carboxyhaemoglobin and methaemoglobin
● Measurement of blood carboxyhaemoglobin can be
used to assess the severity of acute carbon monoxide poisoning and chronic
dichloromethane poisoning.
● Methaemoglobin (oxidized haemoglobin) may be
formed after overdosage with dapsone and oxidizing agents such as chlorates or
nitrites, and can be induced by exposure to aromatic nitro compounds.
(d)
Erythrocyte volume fraction (haematocrit):
- Acute or acute-on-chronic overdosage
with iron salts, acetylsalicylic acid, indometacin, and other nonsteroidal
anti- inflammatory drugs may cause gastrointestinal bleeding leading to
anaemia.
- Anaemia may also result from chronic
exposure to toxins that interfere with haem synthesis, such as lead, or induce
haemolysis either directly (arsine, see arsenic).
(e)
Leukocyte count
- Increases in the leukocyte (white blood
cell) count often occur in acute poisoning, for example, in response to an
acute metabolic acidosis .
Determination of therapeutic drugs
and drugs of abuse
(a) for
treatment of drug toxicity
(b) for
forensic analysis.
(c) for
determination of the levels of drugs for
dosage adjustment
1- Drugs of abuse
Therapeutic
drugs
Type
of Drugs
|
Therapeutic
level
|
Toxic
level
|
Valporic
acid (Depakine)
|
50-100 µg/ml
|
> 100
- 150 µg/ml
|
Carbamazpine
(Tegretol)
|
4.0 – 12.0 µg/ml
|
> 12
µg/ml
|
Digoxin
|
0.9 - 2
µg/ml
|
> 2
µg/ml
|
Theophylline
|
10 – 20
µg/ml
|
> 20
µg/ml
|
Basic techniques for detecting drugs in serum and urine
1- visible and ultraviolet spectrophotometry
The major problem encountered with this technique is interference
2- Thin-layer chromatography (TLC):
qualitative & confirmatory test
3- Enzyme Immunoassays (EMIT):
his assay can detect drug levels in the nanomolar range and is both higly sensitive and specfic.
4- High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): Preparative
HPLC & analytical HPLC. Not limited by the volatility or stability of the sample compound
5- Gas chromatography- mass spectrometry (GC/MS): Gold
standard technique to confirm the results obtained using EMIT and
TLC because of its great sensitivity and its reliability. This technique
is used in the forensic analysis.
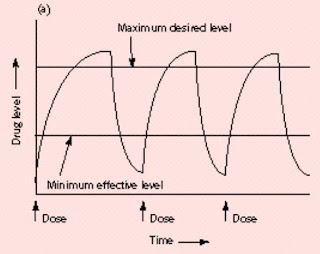
Drug levels in the blood with traditional drug dosing



Thanks for ones marvelous posting! I actually enjoyed reading it, you
ReplyDeletemay be a great author.I will be sure to bookmark your blog and definitely will
come back at some point. I want to encourage you continue your great writing, have
a nice afternoon!
Here is my site :: Louis Vuitton Bags
You actually make it appear so easy along with your presentation however I to find this matter to be really something
ReplyDeletewhich I think I might by no means understand. It seems too complicated and extremely huge for me.
I am taking a look ahead to your next submit, I'll try to get the hang of it!
Have a look at my page ... Sac Louis Vuitton Pas Cher
I love reading through a post that can make men and women
ReplyDeletethink. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
Here is my web site :: Louis Vuitton Purses Outlet
If you would like to get a great deal from this paragraph then you have to apply these
ReplyDeletemethods to your won blog.
Review my blog Nike Free 3.0 (http://ngosummit.com)
Excellent blog right here! Also your web site a lot
ReplyDeleteup very fast! What host are you the usage of? Can I get your associate hyperlink to your host?
I desire my web site loaded up as quickly as yours
lol
Feel free to visit my blog post :: Sac A Main Louis Vuitton